Technology
Foodchain ecosystem
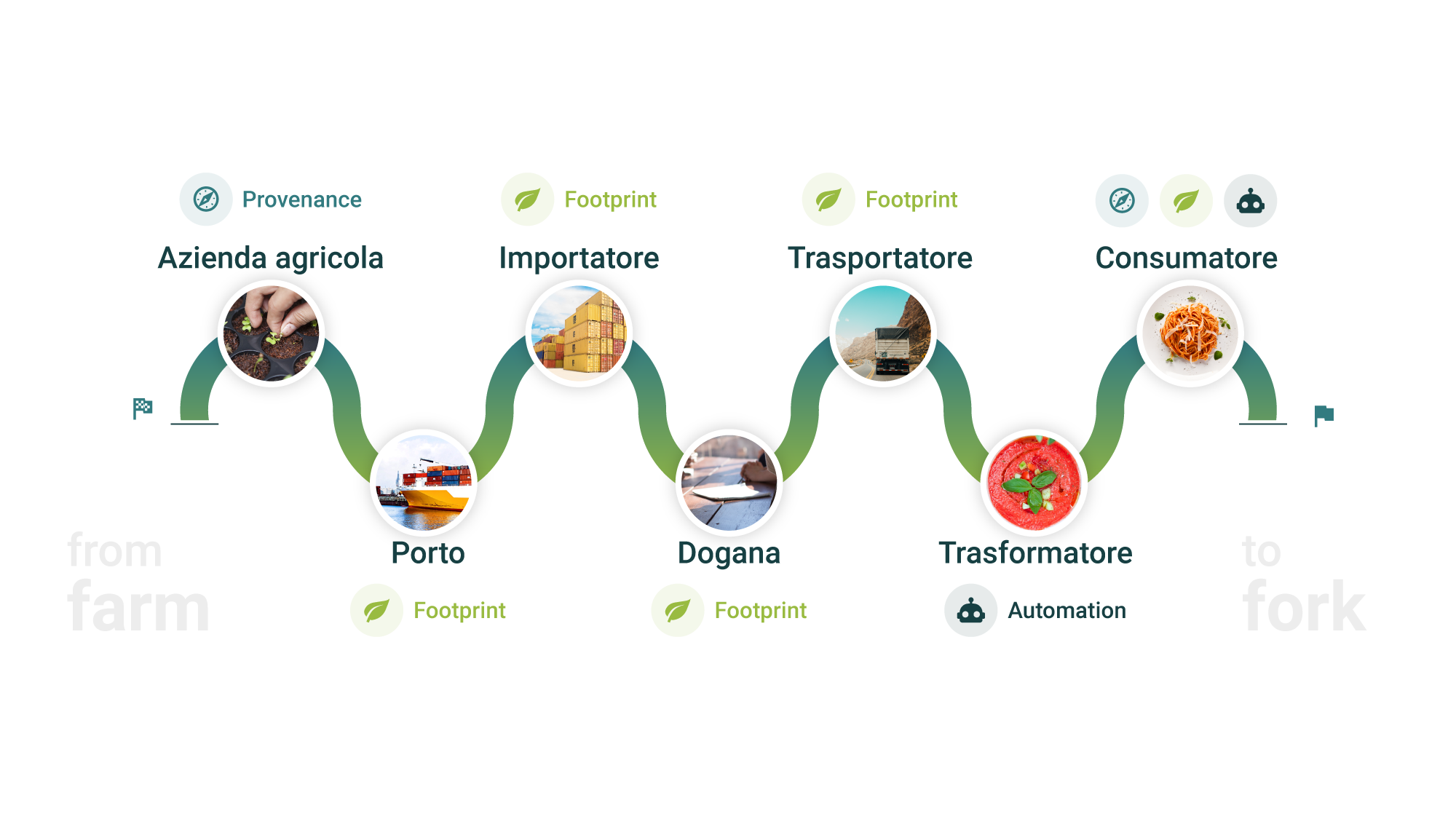
Blockchain is a tool that adds value to your product. Our service allows you to track your product “from farm to fork”: transparency means cooperation from the producer to the consumer.
solutions
Whom we address to

Producers
To show authenticity by communicating all information of a product, from origin of raw materials, to farming and breeding methods, to packaging of the finished product.

Public Administration
A blockchain-based model for traceability is an effective tool for fighting fraud and prevent counterfeiting of “Made in”

Transport
Verify at any time the location of the products, their status and that the delivery is made within the set timeframes.

MMR
To allow consumers to verify the origin of the product alongside the chain and justify the purchase of a high quality product.

Logistic
Demonstrate the quality of the warehouses, the timing and storage of the products, the organization of deliveries.

Certification Authorities
To use a tool to integrate a certification which also enhances ease of auditing and speeds up procedures for quality control.
solutions
The consumer
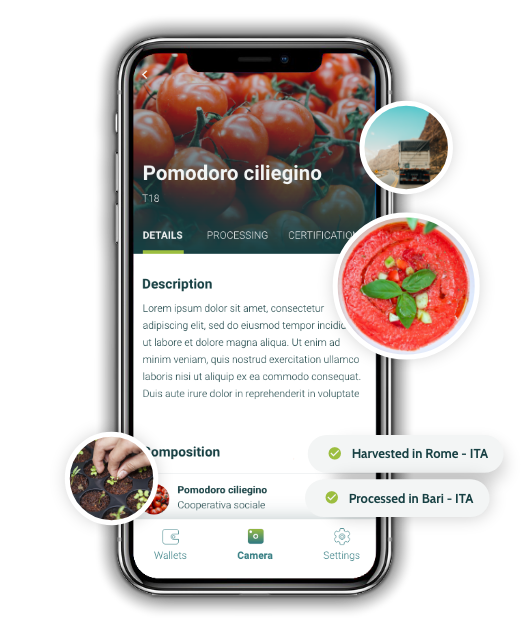
mobile ready
A story in the palm of your hand
Foodchain's QR codes allow you to access the full and immutable story of a product to discover its real path throughout all supply chain processes..
The blockchain connects all the information of the value chain, it crystalizes it and made it available to any user equipped with smartphone and QR codes reader. Through Foodchain's platform all documents, photos, videos and other details related to the product are immediately available.
 Authenticity
Authenticity Sustainability
Sustainability Food safety
Food safety Quality assurance
Quality assurance